Project 5: Screenings for new drugs against schistosomes and liver flukes
Background – DRUID against NTDs
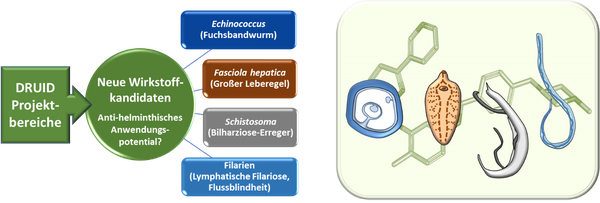
The LOEWE center "DRUID" stands for Novel Drug Targets against Poverty-related and Neglected Tropical Infectious Diseases. Here, leading research groups throughout Hesse focus on the discovery of active substances and diagnostics against tropical infectious diseases (see https://www.loewe-druid.de/). Among the Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs), infections with parasitic worms (helminths) cause the highest health impairment among people worldwide (WHO). In addition to the severely limited spectrum of antiparasitic drugs and a lack of vaccines, also suboptimal therapeutic success and resistance make the development of new agents urgently necessary.
How we discover new drug candidates
As part of our platform project at DRUID, we test novel drug candidates against liver flukes and schistosomes and coordinate tests against a variety of other helminths in laboratories of our global collaborative partners. Noteworthy are the protein kinase inhibitor imatinib and arylmethylamino steroids, for which our platform project has demonstrated a broad antiparasitic spectrum (Li et al. 2019).
Furthermore, our research group is pioneering in the identification of anthelminthic candidates derived from natural products produced by insects, a vast and so far relatively neglected bioresource (Gallinger et al. 2022, Kellershohn et al. 2019, Tonk et al. 2020). We are supported in this endeavor by collaborative partners from the Fraunhofer Institute for Molecular Biology and Applied Ecology.
In addition to substance screenings, we characterize promising drug targets using molecular methods. The target proteins include GPCRs, protein kinases, aldehyde dehydrogenases, autophagy proteins, and a calcium channel (Beutler et al. 2023, Houhou et al. 2019, Mughal et al. 2021 and 2022). In collaboration with the Spengler research group, AP-MALDI mass spectrometry imaging is employed, an innovative imaging method that sheds light on the uptake and metabolism of drugs in the parasite (Mokosch et al. 2021, Morawietz et al. 2020 and 2022).
Through this platform project, we are creating the ideal conditions for identifying substances with a broad antiparasitic spectrum.
Relevant publications on the topic
Eigene Publikationen zum Thema
Beutler M, Harnischfeger J, Weber MHW, Hahnel SR, Quack T, Blohm A, Ueberall ME, Timm T, Lochnit G, Rennar GA, Gallinger TL, Houhou H, Rahlfs S, Falcone FH, Becker K, Schlitzer M, Haeberlein S, Czermak P, Salzig D, Grevelding CG. Identification and characterisation of the tegument-expressed aldehyde dehydrogenase SmALDH_312 of Schistosoma mansoni, a target of disulfiram. Eur J Med Chem (2023) 251:11517
Gallinger TL, Aboagye SY, Obermann W, Weiss M, Grünweller A, Unverzagt C, Williams DL, Schlitzer M, Haeberlein S. First in silico screening of insect molecules for identification of novel anti-parasitic compounds. Pharmaceuticals (2022) 15(2):119
Houhou H, Puckelwaldt O, Strube C, Haeberlein S. Reference gene analysis and its use for kinase expression profiling in Fasciola hepatica. Sci Rep (2019) 9:15867
Kellershohn J, Thomas L, Grünweller A, Hartmann RK, Hardt M, Vilcinskas A, Grevelding CG, Haeberlein S. Insects in anthelminthics research: Lady beetle-derived harmonine affects survival, reproduction and stem cell proliferation of Schistosoma mansoni. PLoS Negl Trop Dis (2019) 13: e0007240
Li X, Haeberlein S, Zhao L, Mughal MN, Zhu T, Liu L, Fang R, Zhou Y, Zhao J, Grevelding CG, Hu M. The ABL kinase inhibitor Imatinib causes phenotypic changes and lethality in adult Schistosoma japonicum. Parasitol Res (2019) 118: 881-890
Mokosch A, Gerbig S, Grevelding CG, Haeberlein S*, Spengler B*. High-resolution AP-SMALDI MSI as a new tool for drug imaging in Schistosoma mansoni. Anal Bioanal Chem (2021) 413:2755-2766
Morawietz CM, Houhou H, Puckelwaldt O, Hehr L, Dreisbach D, Mokosch A, Roeb E, Roderfeld M, Spengler B*, Haeberlein S*. Targeting kinases in Fasciola hepatica: anthelminthic effects and tissue distribution of selected kinase inhibitors. Front Vet Science (2020). 7:611270
Morawietz CM, Peter Ventura AM, Grevelding CG, Haeberlein S*, Spengler B*. Spatial visualization of drug uptake and distribution in Fasciola hepatica using high-resolution AP-SMALDI mass spectrometry imaging. Parasitol Res (2022) 121(4):1145-1153
Mughal MN, Grevelding CG, Haeberlein S. First characterization of autophagy-related genes in Schistosoma mansoni. Int J Parasitol (2021) S0020-7519:00092-8
Mughal MN, Grevelding CG, Haeberlein S. The anticancer drug imatinib induces autophagy in Schistosoma mansoni. Int J Parasitol (2022) 52(4):211-215
Tonk M, Vilcinskas A, Grevelding, CG, Haeberlein S. Anthelminthic activity of assassin bug venom against the blood fluke Schistosoma mansoni. Antibiotics (2020). 9: 664
